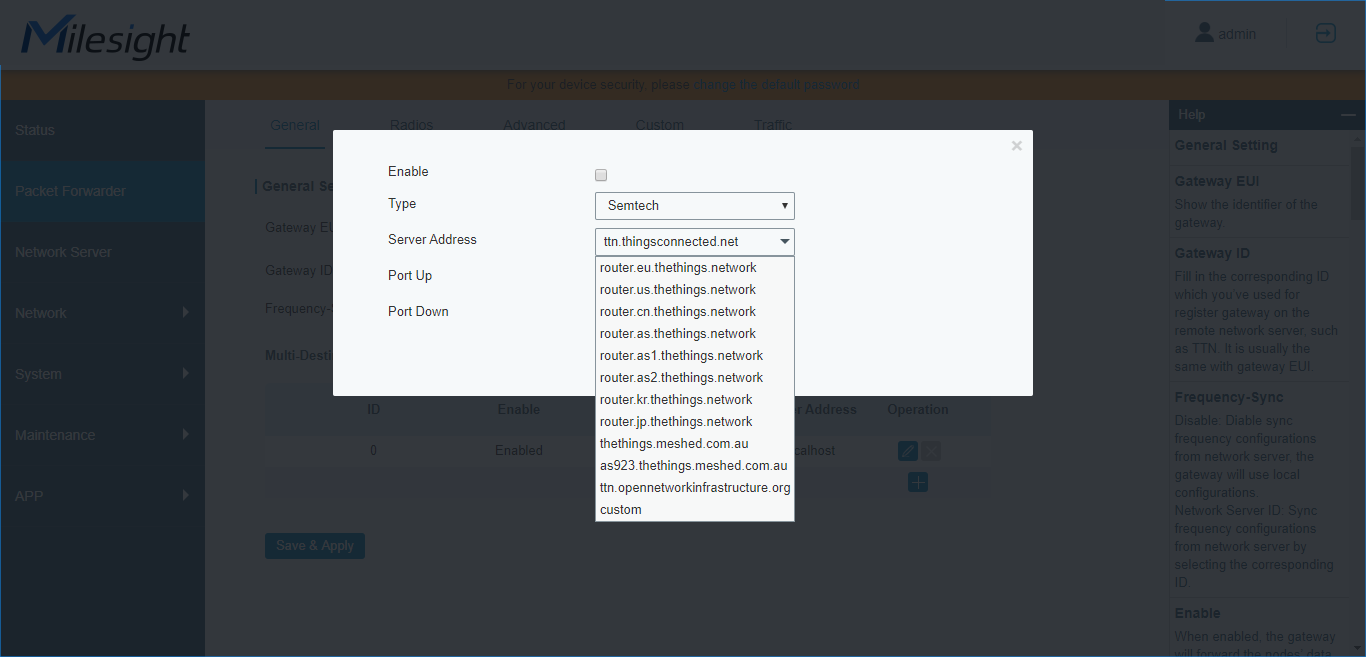
What Is Packet Forwarder?
The packet forwarder is a program running on the host of a LoRa gateway that forwards RF packets received by the concentrator to a server through an IP/UDP link, and emits RF packets that are sent by the server. It can also emit a network-wide GPS-synchronous beacon signal used for coordinating all nodes of the network. Currently, Milesight LoRaWAN® Gateway supports the following packet forwarders:- Semtech
- TTN (how to connect Milesight gateway to TTN)
- Loriot
- ChirpStack-Generic
- Milesight
Semtech UDP Protocol
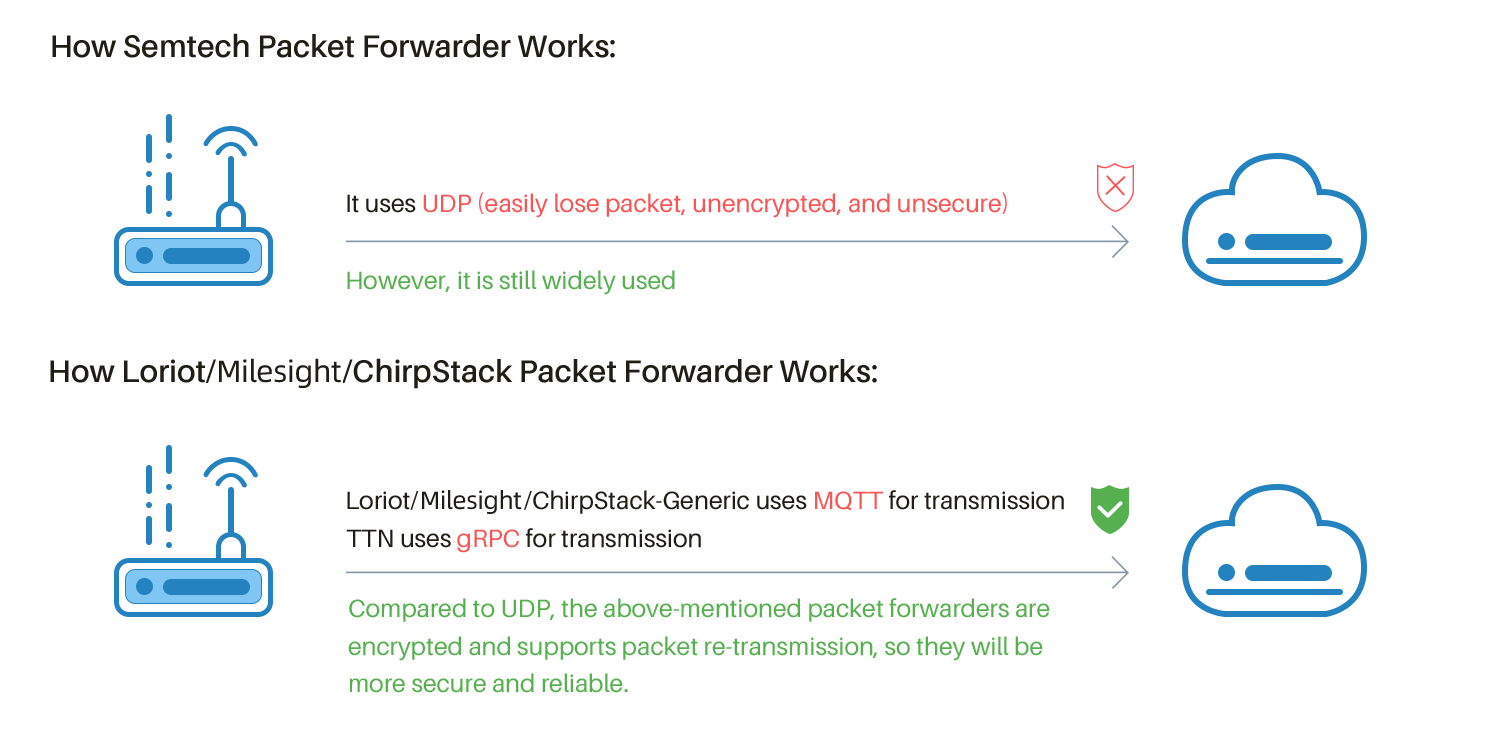
The Semtech UDP protocol is, historically, the first gateway protocol that was developed for LoRaWAN®. It was built by Semtech, who still maintain it. With this protocol, uplinks, statuses and downlinks are exchanged in a pseudo-JSON format, through UDP, between the gateway and the network server. Because of the simplicity of the messages and of the protocol, it is easy to reproduce this protocol, for testing purposes or for bootstrapping. Because this protocol was implemented in the first packet forwarder publicly available, most gateways include a basic packet forwarder running this protocol.Source: Semtech
Drawbacks of the UDP Protocol
However, this protocol lacks features for production-ready networks:- It does not provide authentication. Gateways are supposed to identify themselves with their EUI - but anyone can usurp another gateway.
- There is no encryption available. Gateway messages can be intercepted - and modified - during transport.
- The message exchange is not reliable since the exchange is over 2-way UDP.
- The UDP protocol is based on a format close to JSON, but not fully compliant; for example, the specs specify that an object can hold multiple properties with the same index. This makes it easy to write by hand for testing purposes, but difficult to parse in some situations.
Source: Semtech
TTN Gateway Connector Protocol
TTN has developed a new protocol: the gateway connector protocol. With this protocol:- Gateways are identified by an ID and by a key. Sending a message to a router requires to know the combination.
- Messages are encoded in protocol buffers while being sent. This serialization technology allows the transfer of data from a program to another, in native types, regardless of the language.
Source: TTN
LORIOT Gateway Binary
Read more about custom LORIOT packet forwarder- JSON or compressed BSON based protocol over TCP
- Only HTTPS traffic (port 443)
- TLS v1.2
- Standard certificate-based mutual authentication
- AES encryption
- Easy to setup on any type of network
- Network failover (e.g. 3G / 4G to Ethernet and back)
- Full remote control from the dashboard
- Full remote configuration from the dashboard
- Remote parameterized spectrum scan
- Remote access via SSH tunnel
- Remote monitoring via SNMP tunnel
- Remote commands (bulk reboot, bulk update, bulk firewall changes)
- Self-updating, maintenance-free operation
- Advanced downlink planning and queuing for maximum downlink capacity
- Advanced uplink queuing for zero data loss and scale-out
- Can poll local sensors and operating system parameters
- Can monitor CPU, RAM and storage usage
- Support for legacy USB-based radio front-ends
- Support for both v1.x and v2.x LoRa gateway hardware
Source: Loriot
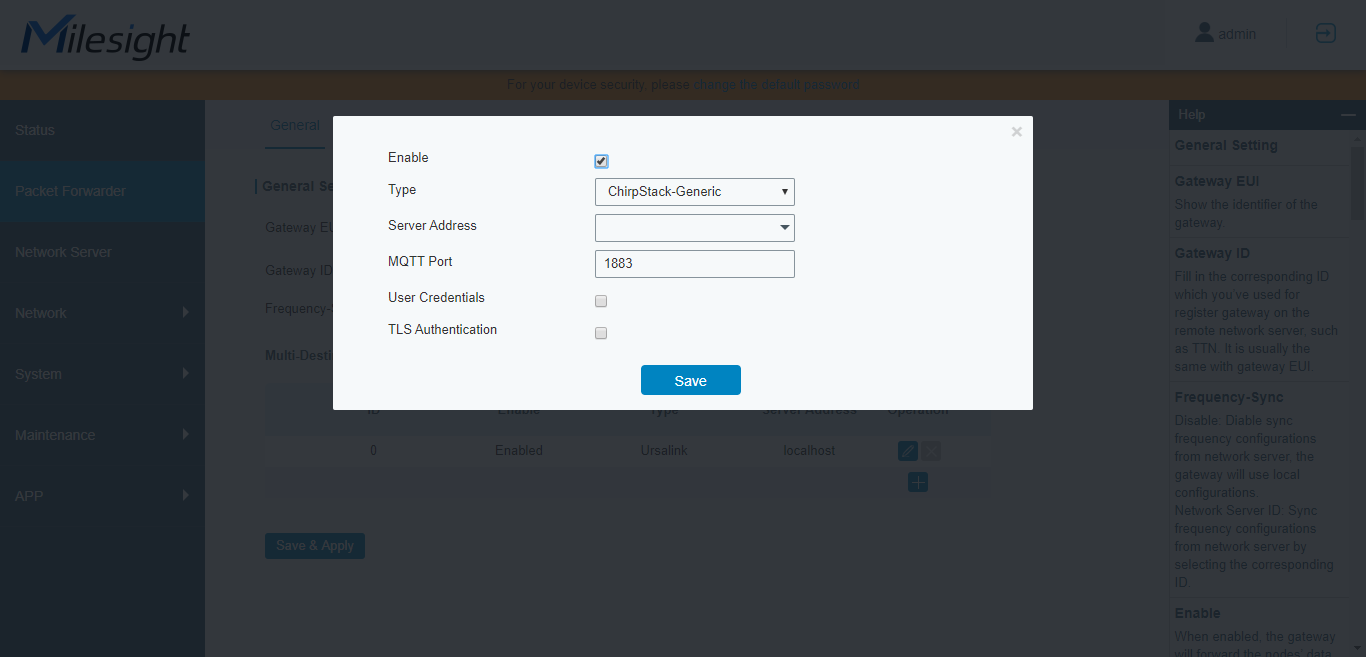
ChirpStack Gateway Bridge
ChirpStack Gateway Bridge has the following advantages:- MQTT (using TCP) over UDP
- Authentication
- SSL/TLS
Source: ChirpStack
Milesight
Packet-forwarding to embedded network server on LoRaWAN® gateway is available when more secure and convenient data transmission needed to forward data/packet locally. Benefits of Milesight Embedded Network Server:- Quick Network Setup & Easy Operation Management
- Save Investment & Boost Business
- Full Integration into Milesight LoRaWAN® Gateway
- Real-Time Data Collection & Processing
- Ready for Future Upgrade