Message Queuing Telemetry Transport protocol, or we can say MQTT protocol, is a messaging protocol based on the lightweight, publish-subscribe network model. It runs over the TCP/IP and provides ordered, lossless, and bi-directional connections, and does not explicitly support the request-response message exchange pattern. Milesight LoRaWAN® gateway with the embedded LoRaWAN® Network Server software support MQTT message forwarding. It can forward the sensor data from LoRaWAN® network to MQTT Broker(Server), and vice versa.
Based on that understanding, MQTT-enabled gateway is a LoRaWAN® gateway that supports MQTT forwarding, then why it is so important to a LoRawan gateway?
Features
- Use the publish-subscribe message model to provide one-to-many message publish and decoupled applications;
- There are three Quality of Service (QoS) levels:
- "At most once"- delivery message at most once, where messages arrive according to the best efforts of the underlying TCP/IP network, which means that message loss or duplication, introduced by software or other causes, can occur. It doesn't matter in some applications as the transmission of the message will be performed again, such as in the environmental monitoring, temperature monitoring.
- "At least once"- deliver message at least once, which guarantees that a message is delivered at least one time to the receiver, but duplicates may occur.
- "Exactly once"- deliver message exactly once, which guarantees that each message is arrived and received only once. This QoS level can be used in the application like billing and meter reading to avoid the incorrect results caused by the message duplication or missing.
- Small transmission and a small header, whose fixed-length is just 2 bytes, and protocol exchanges are minimized to reduce network traffic.
- Use plain text to transmit security credentials.
- Provide network connection over TCP / IP
- Use the Last Will and Testament (LWT) feature to notify other clients about an ungracefully (without a message) disconnected client
Based on the above features, MQTT protocol is perfectly applied into the IoT solutions with very "Low-bandwidth and unreliable links". It also becomes an important function in the network server software embedded in Milesight LoRaWAN® gateways.
The Network Structure for MQTT Forwarding:
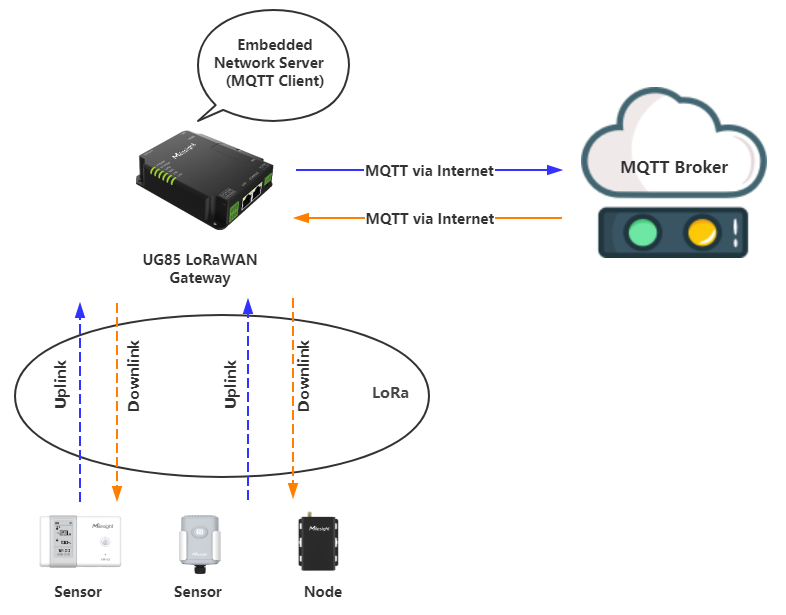
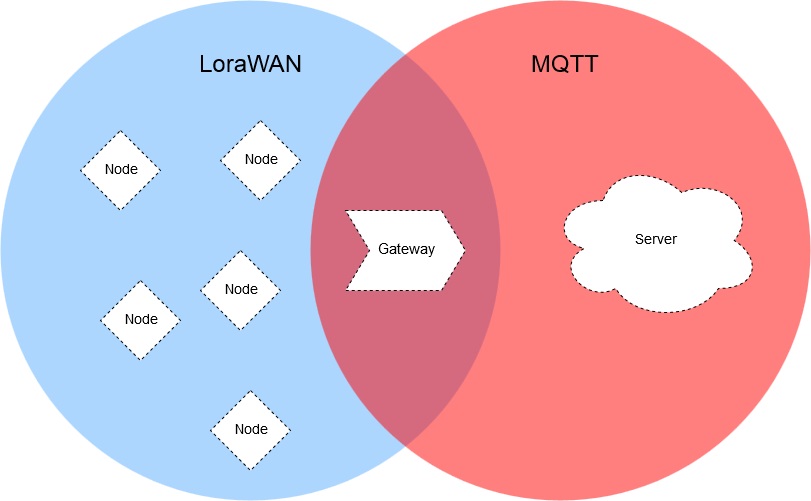
- Sensor Nodes using LoRaWAN®, do not have to bother with MQTT or with the MQTT Server. They just send/receive data to/from the LoRaWAN® gateway. The gateway is the end of those sensors’ world.
- The LoRaWAN® gateway, or more specifically the embedded network server software, is in the intersection of the two sets, LoRaWAN® and MQTT. Its task is to forward the collected data from the local LoRaWAN® sensors/nodes to the MQTT Broker by publishing the appropriate data to a specific MQTT topic, and subscribing a topic in the MQTT Broker when there’s an update on this topic, the gateway will know and broadcast the data back to the local sensors/nodes.
- The MQTT Broker has nothing to do with the local LoRaWAN® network.
Solution:
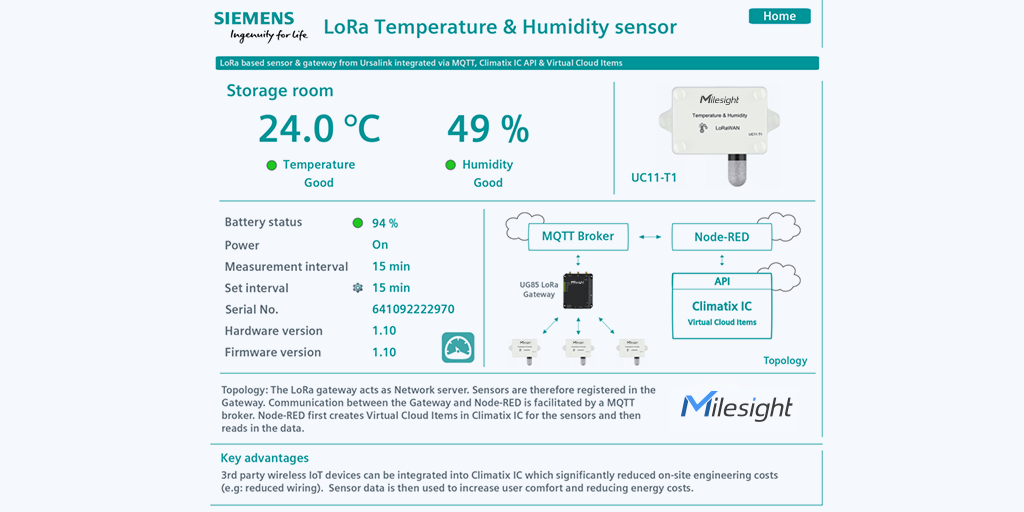
In this PoC project, UC11-T1 and Milesight UG85 indoor gateway are integrated with Siemens’ demo-site for the cloud-based solution Climatix IC platform. The communication between the gateway and Node-RED is facilitated by MQTT Broker. Thanks to the embedded Network Server software, the UG85 gateway works as an MQTT Client here to send/receive messages via MQTT protocol on the Internet.
Key Benefits:
- Highly efficient information distribution
- Increased scalability
- Reduction in network bandwidth consumption dramatically
- Well suited for remote sensing and control
- Permission-based security and time-saving in software development










